
Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications are designed to eliminate the need for intermediaries in everyday financial transactions.
Contents
DeFi – What is it?
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance, it’s a new financial system built on top of blockchain technology such as Ethereum. It enables peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries. It offers a wide range of financial services, and its decentralized nature provides greater accessibility, lower costs, and higher security.
DeFi offers a wide range of financial services including lending, borrowing, trading, and insurance. The use of smart contracts on blockchain networks allows DeFi to provide transparent and secure financial services.
How does DeFi Work?
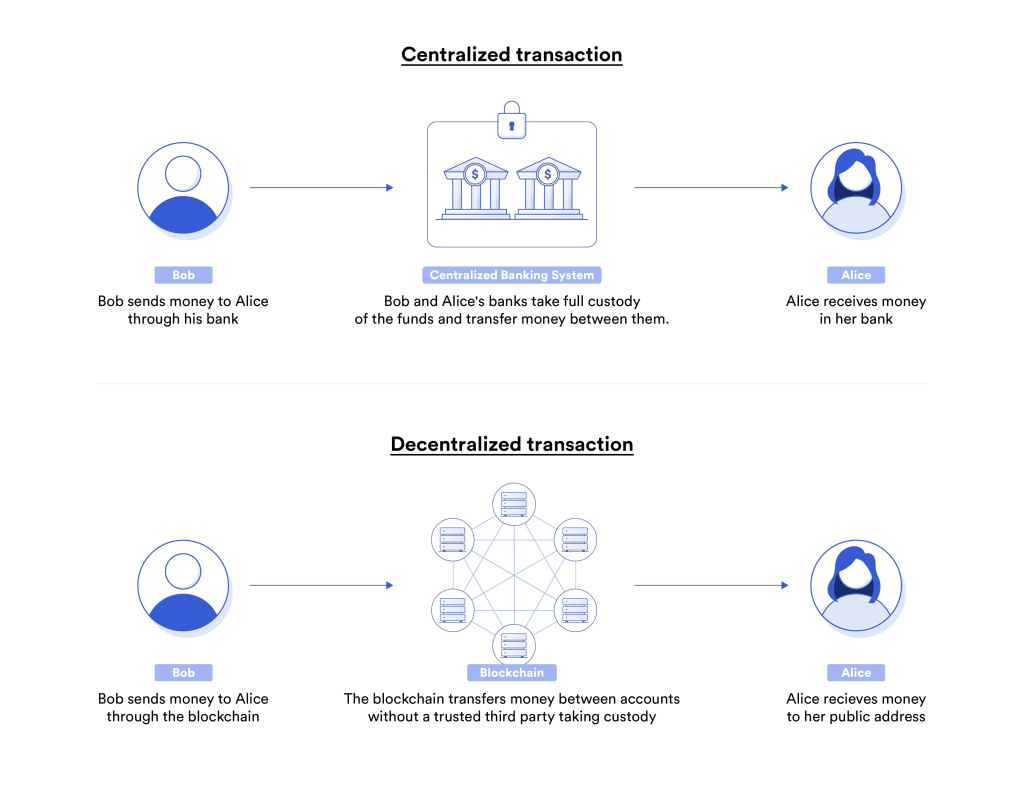
At its core, DeFi is built on blockchain technology, which is a decentralized, digital ledger that records transactions in a transparent and secure way. Blockchain technology allows for the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) that can be accessed by anyone with an internet connection (We will explain more on how this works later). These dApps are built on top of blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, and they use smart contracts to automate financial transactions.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that contain the terms of an agreement between parties and automatically enforce those terms when certain conditions are met. For example, a smart contract could be set up to automatically transfer a certain amount of cryptocurrency from one person to another when a specific date and time is reached. The terms and conditions of the contract, such as the amount of cryptocurrency to be transferred, are encoded into the contract and are automatically enforced by the blockchain network. This eliminates the need for intermediaries such as lawyers or notaries, and it reduces the potential for errors or disputes.
One of the key advantages of DeFi is that it allows individuals to access financial services without the need for centralized intermediaries, such as banks or financial institutions. This means that individuals can access financial services without having to go through traditional financial gatekeepers, which can be costly and time-consuming. Additionally, DeFi provides greater transparency and security compared to traditional financial systems, as all transactions are recorded on a public blockchain and can be easily audited.
Decentralized Lending Platforms
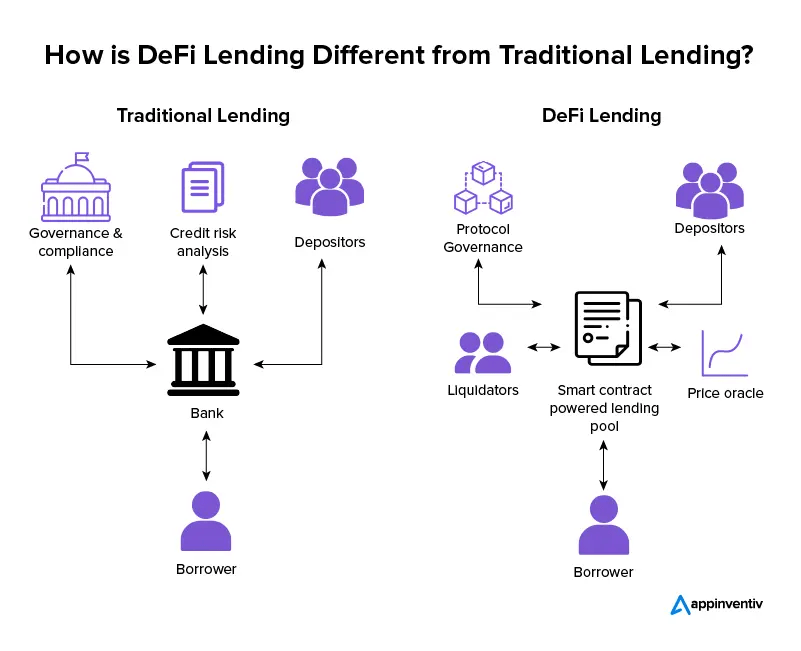
DeFi works by connecting borrowers and lenders directly, without the need for intermediaries. This is done through decentralized lending platforms, such as Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO, which allow individuals to lend and borrow assets, such as cryptocurrency, in a peer-to-peer manner. These platforms use smart contracts to automate the lending process, and they typically require borrowers to provide collateral in order to secure a loan. This collateral is held in a smart contract, and it is automatically liquidated if the borrower is unable to repay the loan.
DeFi lending platforms also offer a high degree of transparency and security, as all transactions are recorded on a public blockchain and can be easily audited.
- Let’s say you have 1,000 USD in cryptocurrency that you would like to lend out on a DeFi lending platform. The platform may offer an annual interest rate of 10%. This means that after one year, you would have earned 100 USD in interest (1,000 x 10%).
- Many DeFi lending platforms offer higher interest rates than traditional banks, and they allow you to earn interest on a wide range of assets, including cryptocurrency and stablecoins, which can be beneficial for diversifying your portfolio.
Decentralized Exchanges

In addition to lending and borrowing, DeFi also enables individuals to trade assets in a decentralized manner. This is done through decentralized exchanges (DEXs), such as Uniswap, Kyber Network, and 0x, which allow individuals to trade assets without the need for centralized intermediaries. DEXs typically use smart contracts to match buyers and sellers, and they typically have lower fees compared to centralized exchanges.
An example of a Decentralized applications (dApp) is Uniswap which is also a DEX built on the Ethereum blockchain. Uniswap allows users to trade cryptocurrencies in a decentralized manner, without the need for a centralized intermediary. Users can connect to Uniswap through their digital wallet, such as MetaMask, and can trade various ERC-20 tokens (used to create and issue smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain). Uniswap uses an automated market maker (AMM) algorithm, which allows users to trade tokens directly with each other and eliminates the need for an order book
Additionally, Uniswap also allows users to provide liquidity to the platform and earn a share of the trading fees as a reward. This is done by depositing a certain amount of token into Uniswap’s liquidity pool and earn liquidity provider tokens in return. These tokens represent the user’s share of the liquidity pool and they can be staked to earn a share of the trading fees.
Uniswap is a good example of a dApp because it is built on a decentralized blockchain network, it operates without the need of centralized intermediaries, and its code is open-source, which allows for transparency and security.
Yield Farming
Another important aspect of DeFi is the concept of yield farming, which is a process of earning interest on assets by lending them out on decentralized lending platforms. Yield farming allows individuals to earn interest on their assets while also providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges. This is done by lending assets to decentralized lending platforms, and then using those assets to provide liquidity to decentralized exchanges. The interest earned on the assets is then distributed to the liquidity providers as a reward for providing liquidity.
Getting Started In Defi

To get started with DeFi, it is important to have a basic understanding of blockchain technology, as well as the different types of DeFi applications and platforms that are available. It is also important to have a digital wallet, such as MetaMask, that supports the blockchain network that you plan to use.
Once you have a digital wallet, you can start exploring the different DeFi applications and platforms that are available. A good starting point would be to visit a decentralized lending platform, such as Aave or Compound, and start experimenting with lending and borrowing. You can also visit a decentralized exchange, such as Uniswap or Kyber Network, and start experimenting with trading.
Risks of DeFi
As you explore the DeFi space, it’s also important to keep an eye on the risks involved. One of the biggest risks in DeFi is the potential for smart contract bugs and vulnerabilities, which can lead to the loss of funds. It’s important to be cautious when interacting with smart contracts and to always double-check the code before sending any funds. Additionally, DeFi platforms and applications are often built on top of Ethereum, and the high gas fees associated with the Ethereum network can make some transactions cost-prohibitive.
Another important aspect of DeFi is the concept of governance. Many DeFi applications and platforms are governed by their respective communities, and individuals can participate in governance by holding and staking the platform’s native tokens. This allows individuals to have a say in the direction and development of the platform. However this can be risky because what communities and individuals vote for could have a negative impact on your tokens.
It’s important to note that lending on DeFi platforms also carries some risks such as volatility of the crypto market, smart contract bugs and the ability to lose the assets if the borrower does not pay back the loan. It’s crucial to always do your own research and understand the platform and the risk involved before lending out assets.
Conclusion and Future Scope
Understanding DeFi cannot be done by reading this blog. Here are some future topics that will be written to help your journey into DeFi.
- Stablecoins in DeFi: Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency that are pegged to a stable asset, such as the US dollar. They are increasingly being used in DeFi for lending, borrowing, and trading.
- Yield Farming: Yield farming is a process of earning interest on assets by lending them out on decentralized lending platforms. Understanding how yield farming works and the different platforms that offer it can help individuals earn higher returns on their assets.
- Setting up a DeFi Wallet: Setting up a digital wallet that supports the blockchain network you plan to use is an essential step in getting started with DeFi.
- Setting up a DeFi Portfolio: Setting up a diversified DeFi portfolio can help individuals maximize their returns and minimize their risks. Understanding how to create a portfolio, how to rebalance it, and how to track its performance can help individuals make the most of their DeFi investments.
- Connecting to DeFi Platforms: Once you have set up your digital wallet, you can start exploring the different DeFi applications and platforms that are available.
As the DeFi ecosystem is constantly evolving, it’s important to stay informed and keep learning about new developments and trends in the space.
In conclusion, DeFi is a rapidly growing segment of the blockchain and cryptocurrency industry that aims to disrupt traditional financial systems by providing decentralized, transparent, and accessible financial services. It is built on blockchain technology and enables individuals to access a wide range of financial services without the need for centralized intermediaries. While DeFi has the potential to revolutionize the financial industry, it is important to be aware of the risks involved and to stay informed about the latest developments. With the right knowledge and tools, anyone can participate in the DeFi revolution and access the benefits it has to offer.


Quite informative. Thanks for sharing the knowledge in a simplified format. Well appreciated.
LikeLike